Looking for Best Laparoscopic Surgeons In Vijayawada? MIG Hospital provides Laparoscopic Surgery at reasonable cost. Visit our Best Laparoscopy Surgery Hospital in Vijayawada or book appointment now.
Laparoscopic surgery (Minimally invasive surgery)
What is minimally invasive surgery?Minimally invasive surgery is a type of surgery that uses special tools designed to decrease the size of incisions and reduce how much the body’s tissues get damaged.
One kind of minimally invasive surgery involves the use of a “scope,” a viewing device that allows surgeons to look inside the body without opening it up all the way. Another type, called “endovascular surgery,” uses X-rays to see inside the body while the surgeon uses special devices that fit inside the blood vessels. This article is about the type of surgery that involves scopes.
There are several different types of scopes, but they all work in about the same way. They consist of a long, thin tube with a tiny camera and a light on the end. The camera sends pictures of the inside of the body to a TV screen. When doing this type of surgery, the surgeon makes a small incision just big enough for the scope to fit through. They also make 2 or more other incisions that slim tools can fit through. These tools include clamps, scissors, and stitching devices, which the surgeon can control from outside the body. While looking at the picture on the screen, the surgeon uses those tools to do the operation.
Dr. Sure Pavan Kumar is one of the Best Gastroenterologist in Vijayawada with well experienced in Laparoscopic Surgeries.
What are the different types of minimally invasive surgery?
There are lots of different types. Their names are based on the body parts that are involved. The scopes used for the different types of surgery are named that way, too:
⦁ Thoracoscopes are used in the chest for “thoracoscopic surgery.” (“Thorax” is Greek for chest.) This type of surgery can be used to remove pieces of lung or to do certain types of heart surgery.
⦁ Laparoscopes are used in the belly for “laparoscopic surgery.” (“Lapara” is Greek for the space between the bottom of the rib cage and the hips.) This type of surgery can be used to remove the gallbladder, appendix, or uterus, or to do lots of other different procedures.
⦁ Hysteroscopes are used in the uterus and vagina for “hysteroscopic surgery.” (“Hystera” is Greek for uterus.) This type of surgery can be used to remove abnormal growths in the uterus, or to do a number of different procedures on the uterus and vagina.
⦁ Arthroscopes are used inside joints for “arthroscopic surgery.” (“Arthron” is Greek for joint.) This type of surgery can be used to repair or rebuild joints in the knee, shoulder, and hip.
Some minimally invasive surgeries involve a surgical “robot,” which is a machine that the surgeon controls. This is called “robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery” or simply “robotic surgery.” The tools used in robotic surgery allows for more controlled movements than regular tools.
How is minimally invasive surgery different from regular surgery?
In general – but not always – this type of surgery makes recovery easier. That’s because:
⦁ It usually involves several small wounds, rather than one big one
⦁ The organs don’t get moved around as much
Despite all of the differences with regular surgery, minimally invasive surgery is still surgery. People who have it do have some pain, they do often need stitches, and they can develop infections or other problems because of the surgery.
Can people always choose to have minimally invasive surgery?
No.
Many procedures can now be done through a minimally invasive approach. But it’s not entirely up to the person to choose what type of surgery they will have. Whether or not a person can have this type of surgery will depend on:
⦁ Whether there is a surgeon available with enough experience doing the type of surgery the person needs
⦁ Why the person needs surgery. (As an example, people who need surgery to remove very large cancers cannot always have minimally invasive procedures.)
⦁ What other health problems the person might have (As an example, people who have serious heart or lung problems cannot tolerate minimally invasive surgery.)
Even when a person starts out having minimally invasive surgery, there’s no guarantee that the surgery will stay that way. Sometimes surgeons start out doing minimally invasive surgery and then switch to open surgery because they find something unexpected. This doesn’t mean the surgeon has done anything wrong. It is usually done to protect the person’s safety.
Advantages of Laparoscopic Surgery
- The advantages of laparoscopic surgery include:
⦁ Faster Recovery
⦁ Less Pain
⦁ Low Blood Loss
⦁ Less visible scars
⦁ Less chances of infection
⦁ Faster return to work or activity
Procedure of Laparoscopy
⦁ Performed through small holes created in the abdominal wall. The telescope, which is used to visualise organs inside the body, is passed inside the tummy via the navel.
⦁ The abdomen is distended with a gas to make more room. Picture images of the abdominal organs can be viewed on a TV screen.
⦁ It gives visualization and clarity of the internal organs better than that of conventional surgery since the image is magnified.
⦁ Two or three small instruments are passed on the sides along with it to perform the procedure.
Is Laparoscopic surgery expensive ?
NO
⦁ Lack of awareness, inadequately trained surgeons and improperly informed patients are the major problems associated with Laparoscopy.
⦁ People stay away from the procedure thinking that it’s very expensive, but the cost is comparable if we take in to consideration of other factors like duration of hospital stay, complications and return to work
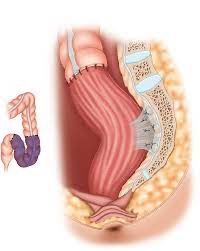
Laparoscopic Appendicectomy
⦁ An appendicectomy (or appendectomy) is the surgical removal of the vermiform appendix.
⦁ This procedure is normally performed as an emergency procedure, when the patient is suffering from acute appendicitis.
⦁ Appendicectomy may be performed laparoscopically or as an open operation. Laparoscopy is often used if the diagnosis is in doubt, or if it is desirable to hide the scars in the umbilicus or in the pubic hair line.
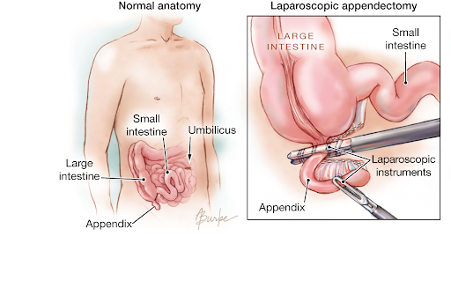
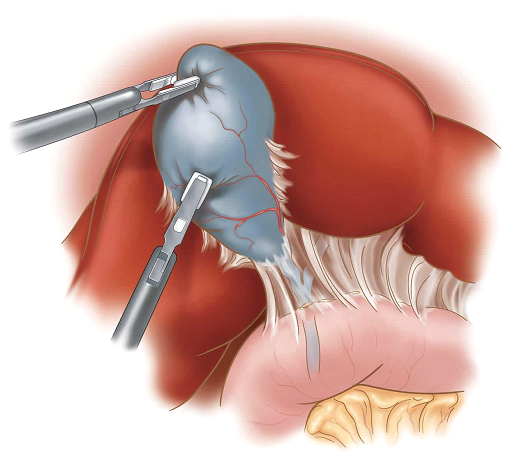
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
- ⦁ Cholecystectomy is the surgical removal of the gallbladder.
- ⦁ Surgery options include the standard procedure, called laparoscopic cholecystectomy, and an older more invasive procedure, called open cholecystectomy.
Laparoscopic CBD Exploration
- ⦁ Common Bile Duct is a tubular structure connecting hepatic duct to the intestine. Obstruction of the bile duct with stones can cause jaundice with fever and chills.
- ⦁ With ERCP, these stones can be removed Laparoscopic CBD exploration is a technically demanding surgery
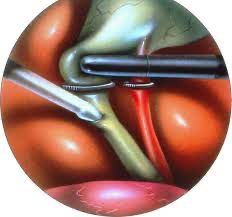
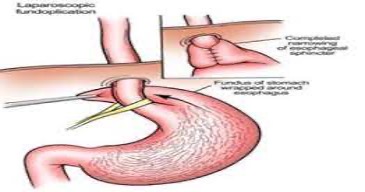
Laparoscopic Hiatus hernia repair
⦁ It is the protrusion (or herniation) of the upper part of the stomach into the thorax through a tear or weakness in the diaphragm.
⦁ The symptoms include acid reflux, and pain, similar to heartburn, in the chest and upper stomach.
⦁ The surgical procedure used is called Nissen fundoplication. In fundoplication, the gastric fundus (upper part) of the stomach is wrapped, or plicated, around the inferior part of the esophagus, preventing herniation of the stomach through the hiatus in the diaphragm and the reflux of gastric acid.
⦁ The procedure is now commonly performed laparoscopically. With proper patient selection, laparoscopic fundoplication has low complication rates and a quick recovery.
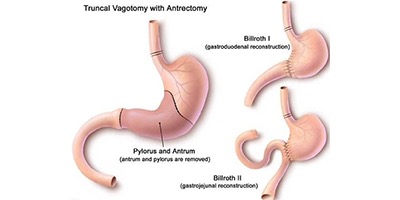
Laparoscopic Vagotomy & drainage procedures
⦁ This procedure is done for Chronic Duodenal Ulcer with scarring causing obstruction of stomach.
⦁ Vagotomy decreases acid production and drainage procedure helps in easy emptying of food contents
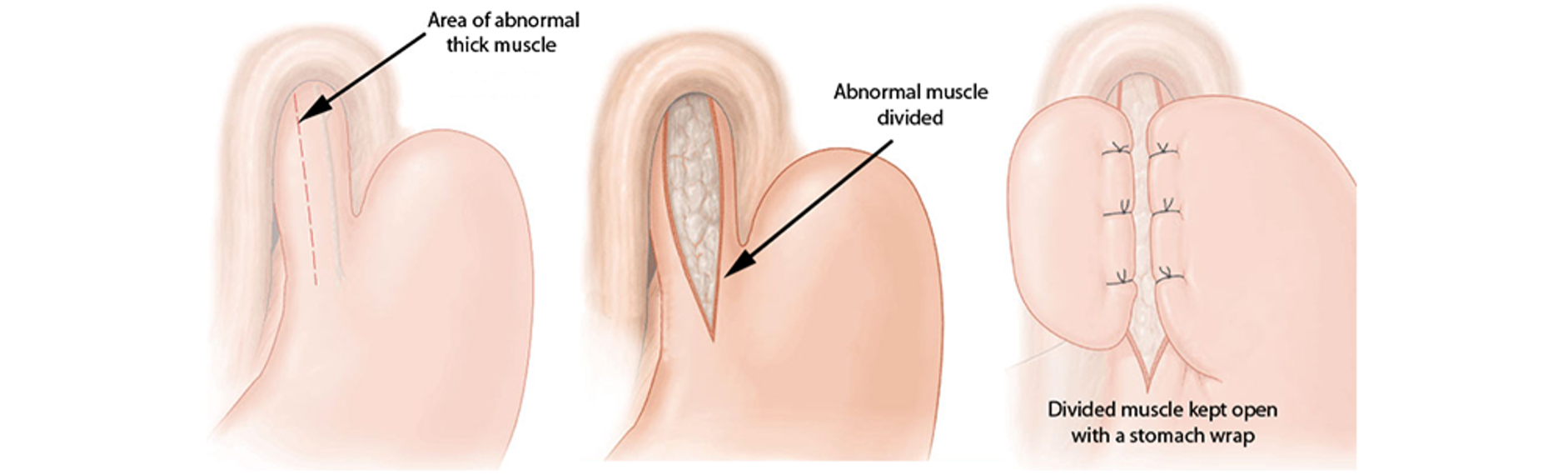
Laparoscopic Cardiomyotomy
⦁ Achalasia Cardia is a condition causing constriction at the junction of the esophagus (Gullet) with stomach.
⦁ Incision of muscles along lower esophagus and stomach helps in easy swallowing by division of muscle which caused constriction
Laparoscopic Splenectomy
⦁ A splenectomy is a procedure that involves the removal of the spleen by operative means.
⦁ Current knowledge of its purpose includes the removal of old red blood cells and platelets, and the detection and fight against certain bacteria. It’s also known to create new blood cells.
⦁ The spleen is enlarged in a variety of conditions such as malaria, mononucleosis and most commonly in “cancers” of the lymphatics, such as lymphomas or leukemia.
⦁ In general, spleens are removed by laparoscopy (minimal access surgery) when the spleen is not too large and when the procedure is elective.
⦁ Splenectomy is done if massive splenomegaly causing decreased appetite, bloating, weight loss due to decreased intake, Gi bleeding, diagnostic purposes and other
Laparoscopic hernia repair
⦁ An incisional hernia occurs when the area of weakness through which the hernia occurs, is the result of an incompletely healed surgical wound.
⦁ These hernias present as a bulge or protrusion at or near the area of the prior incision scar. Virtually any prior abdominal operation can subsequently develop an Incisional Hernia at the scar area, including those from large abdominal procedures (intestinal surgery, vascular surgery), to small incisions (Appendectomy, or Laparoscopy).
⦁ These hernias can occur at any incision, but tend to occur more commonly along a straight line from the breastbone straight down to the pubis, and are more complex in these regions.
⦁ Hernias in this area have a high rate of recurrence if repaired via a simple suture technique under tension and it is especially advised that these be repaired via a TENSION FREE repair method using mesh.
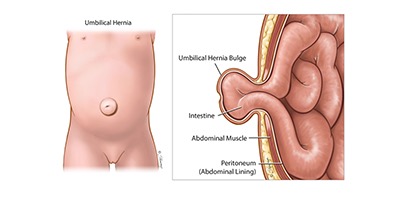
Laparoscopic Umbilical hernia repair
⦁ It is a defect at the level of the umbilicus through which the intestines bulge out. With tension free ‘mesh’ repair umbilical hernia can be effectively managed laparoscopically.
Laparoscopic Inguinal hernia repair
⦁ Laparoscopy is the ‘Gold Standard’ for bilateral hernia and recurrent hernias. This includes repair of the inguinal area with mesh.
⦁ The recurrence rate with laparoscopic mesh repair is almost zero percentage.
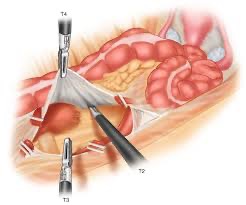
Laparoscopic Assisted colectomy
⦁ This procedure is mainly done for colon cancer. The radicality and extent of the surgery is not compromised while doing a laparoscopic procedure.
Laparoscopic Anterior Resection
⦁ This procedure is done for cancer of the rectum. Anterior Resection by conventional method is a complex procedure involving removal of the cancer of upper rectum with adjacent tissues.
⦁ Nowadays Laparoscopic Anterior Resection is becoming the Gold Standard for rectal cancer because the procedure does not compromise on removing the whole cancer with adjacent tissues.
Laparoscopic Rectopexy
⦁ This is done for full thickness prolapse of the rectum causing swelling at perianal region
⦁ Symptoms include perianal swelling, mucus discharge, itching and bleeding per rectum, constipation